 In this Mulesoft article they introduce the Agentic Enterprise Maturity Model, a framework to guide businesses in adopting AI agents, which are driving a significant technological shift.
In this Mulesoft article they introduce the Agentic Enterprise Maturity Model, a framework to guide businesses in adopting AI agents, which are driving a significant technological shift.
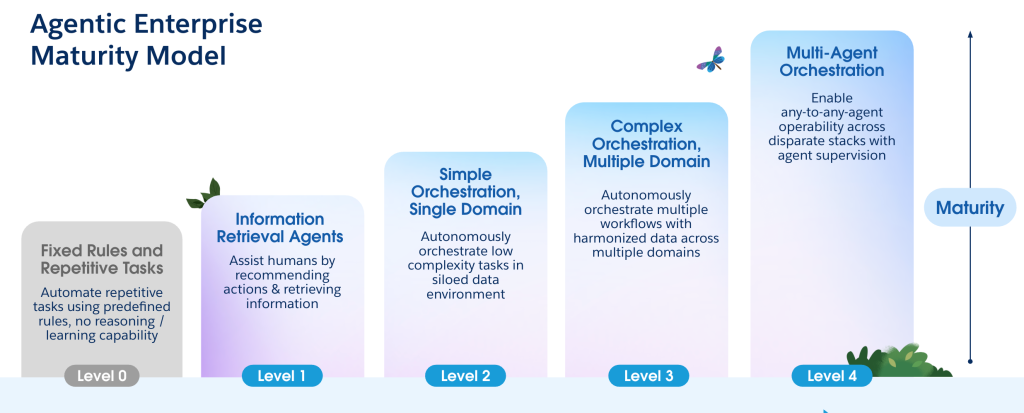
The model helps organizations assess their readiness and progress in integrating AI agents by categorizing their capabilities into four progressive levels, from basic to advanced:
- Level 0 (Pre-GenAI): Basic rule-based chatbots automate repetitive tasks but lack reasoning or adaptability.
- Level 1: AI agents act as information retrieval assistants, quickly finding relevant data and suggesting actions.
- Level 2: Agents handle more complex tasks, such as analyzing data and making recommendations, with some decision-making autonomy.
- Level 3: Agents orchestrate multi-step workflows, integrating with various systems for broader automation.
- Level 4 (Aspirational): Fully autonomous agents manage core business functions with minimal human oversight, requiring reimagined processes, robust risk management, and composable architectures for seamless integration.
The article highlights that while Level 4 represents the future of AI-driven enterprises, adoption remains aspirational due to technical and organizational challenges. Businesses must assess their current level, build capabilities, and leverage composable architectures to enable agentic transformation, ensuring AI agents can dynamically interact with enterprise systems for efficiency and innovation.
Level 4
Level 4 of the Agentic Enterprise Maturity Model, as described in the MuleSoft blog article, represents the aspirational stage of AI agent adoption, where fully autonomous agents manage core business functions with minimal human oversight. At this level, AI agents achieve a high degree of sophistication, enabling transformative operational efficiency and innovation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Full Autonomy: Agents at Level 4 operate independently, executing complex, multi-step processes across enterprise systems without requiring constant human intervention. They can make decisions, adapt to changing conditions, and optimize outcomes in real time.
Core Business Function Management: These agents handle critical operations, such as supply chain optimization, customer relationship management, or financial forecasting, acting as strategic orchestrators rather than just task performers.
Dynamic Integration: Level 4 agents seamlessly integrate with diverse enterprise systems, leveraging composable architectures (modular, interoperable systems) to interact with data, applications, and processes dynamically. This ensures flexibility and scalability.
Advanced Reasoning and Adaptability: Equipped with advanced reasoning capabilities, these agents can analyze complex scenarios, learn from outcomes, and adjust strategies to meet business goals, even in unpredictable environments.
Reimagined Processes: Achieving Level 4 requires organizations to fundamentally redesign business processes to accommodate autonomous agents. This involves rethinking workflows, data structures, and governance models to support AI-driven operations.
Robust Risk Management: Due to their autonomy, Level 4 agents necessitate strong safeguards, including ethical guidelines, compliance frameworks, and monitoring systems to mitigate risks like unintended consequences or bias.
Aspirational Nature: The article notes that Level 4 is not yet widely achieved due to significant technical and organizational challenges, such as building secure, scalable architectures and fostering a culture ready for AI-driven transformation.
In essence, Level 4 envisions a future where AI agents act as trusted, autonomous partners, driving enterprise-wide innovation and efficiency, but reaching this stage demands advanced technology, strategic planning, and organizational readiness.



